- T6 Spinal Cord Injury: Navigating the Challenges and Embracing Resilience
- Sensory Impairment
- Motor Impairment
- Other Complications
- Treatment and Management
- T6 Spinal Cord Injury: Navigating Bladder and Bowel Challenges
- Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction
- T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Autonomic Dysreflexia
- Symptoms of Autonomic Dysreflexia
- Triggering Factors of Autonomic Dysreflexia
- Managing Autonomic Dysreflexia
- Prevention and Prognosis
- T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
- Treatment and Rehabilitation
- Managing Symptoms
- Promoting Mobility
- Improving Quality of Life
- T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Treatment
- Prognosis
- Legal Considerations
- Preventing T6 Spinal Cord Injuries
- T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
- Legal Protections
- Medical Treatment
- Adaptive Equipment
- Support Groups
- Financial Assistance
- Long-Term Care Planning
- Emotional and Psychological Support
- Reablement
- Conclusion
- T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
- Symptoms of a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
- Treatment Options for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
- Rehabilitation for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
- Finding Legal Help
- Emotional Support for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
- Financial Assistance for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
- Living a Fulfilling Life with a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
T6 Spinal Cord Injury: Navigating the Challenges and Embracing Resilience
Imagine the profound impact a spinal cord injury could have on your life, affecting both your physical and emotional well-being. For those who have sustained a T6 spinal cord injury, the upper back and chest bear the brunt of the damage, presenting formidable challenges that demand resilience and adaptation.
Injury Overview
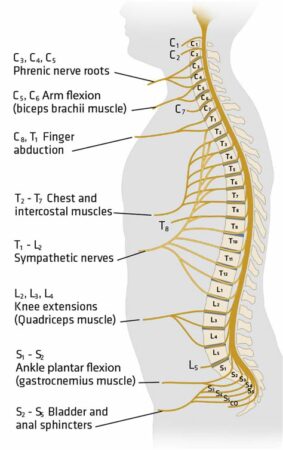
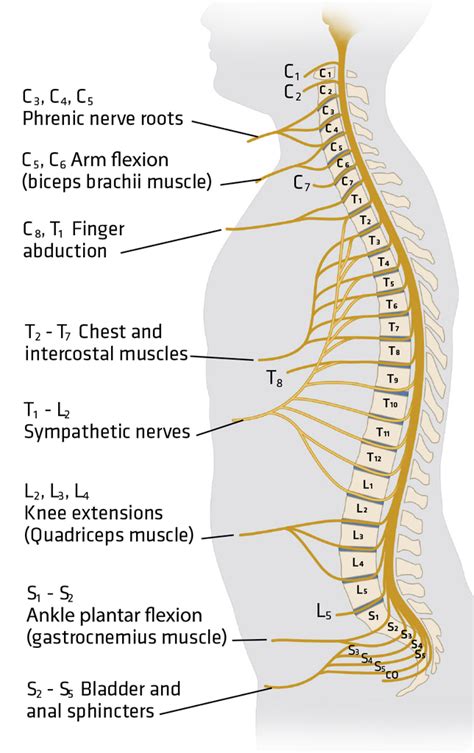
A T6 spinal cord injury occurs when the spinal cord is damaged at or near the T6 level, which is located in the upper thoracic region of the spine. This injury affects the nerves and functions controlled by the T6 spinal segment, leading to varying degrees of paralysis and sensory loss in the arms, chest, and abdomen. Depending on the severity of the injury, individuals may experience complete or incomplete paralysis, affecting their mobility, sensation, and bodily functions.
Impairments and Challenges
T6 spinal cord injuries can result in a wide range of impairments and challenges. Motor function in the arms and hands may be compromised, affecting tasks such as reaching, gripping, and manipulating objects. Sensory loss in the chest and abdomen can impact the ability to feel touch, temperature, and pain. Other potential impairments include decreased respiratory function, impaired bowel and bladder control, and sexual dysfunction.
Coping with these impairments and challenges requires resilience, determination, and a strong support system. Individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries often undergo extensive rehabilitation to regain as much function as possible and learn strategies for managing their limitations.
Physical and Emotional Impact
Beyond the physical impairments, T6 spinal cord injuries can also have a significant emotional impact. Adapting to a new reality, dealing with chronic pain, and navigating social barriers can take a toll on one’s mental health. Depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder are common challenges faced by individuals with spinal cord injuries.
It’s important to acknowledge the emotional weight of such an injury and seek support from loved ones, counselors, and support groups. Emotional resilience is crucial for maintaining a positive outlook and embracing the journey of recovery.
**T6 Spinal Cord Injury: Navigating Life’s New Reality**
In the face of a T6 spinal cord injury, life as you knew it takes a sudden and unexpected turn. This damage to the spinal cord, located between the fifth and sixth thoracic vertebrae, disrupts communication between the brain and the body below the injury site. While every injury is unique, this specific level often impacts mobility, sensation, and bodily functions.
**Effects on Mobility**
A T6 spinal cord injury typically results in a range of mobility impairments. Paralysis or weakness sets in in the legs, abdomen, and pelvic muscles. This diminished functionality can make even basic tasks like walking, standing, or sitting a significant challenge. Individuals may require assistive devices such as wheelchairs, braces, or crutches to regain some degree of mobility. Daily activities like dressing, cooking, or bathing can also become more demanding, requiring modifications and adaptations to accommodate the new physical constraints.
Besides the physical challenges, a T6 spinal cord injury can profoundly affect one’s emotional and mental well-being. The challenges of navigating a world that now feels fundamentally different can test the limits of resilience. However, with the right support and resources, individuals can learn to adapt, rebuild their lives, and find new ways to thrive.
**T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide to the Thoracic Region**
A T6 spinal cord injury, also known as a thoracic injury, affects the sixth thoracic vertebra of the spinal column. This trauma can result in a variety of symptoms and complications, including sensory impairment below the level of the injury.
Sensory Impairment
One significant consequence of a T6 spinal cord injury is sensory loss. This loss can be partial or complete and affects the senses of touch, pain, and temperature. Individuals may experience:
– Numbness and tingling: These sensations often occur in the hands, feet, and other areas of the body below the injury.
– Difficulty sensing pain: This can be a serious risk as individuals may not be aware of cuts, burns, or other injuries.
– Reduced temperature sensation: Individuals may have trouble gauging water temperature or feeling the warmth of a blanket.
The severity of sensory impairment depends on the extent of the spinal cord damage. If the injury is complete, sensation may be lost below the level of the injury, while in incomplete injuries, some sensation may remain.
Motor Impairment
Paralysis is a common complication of a cervical spinal cord injury, ranging from partial to complete paralysis. Individuals with incomplete paralysis may have some movement and sensation in the affected limbs. T6 injuries may result in weakness or paralysis in the trunk, legs, and feet.
Other Complications
In addition to sensory and motor impairments, a T6 spinal cord injury can lead to a host of other complications. These may include:
– Autonomic dysreflexia: This condition can lead to high blood pressure, headaches, and sweating.
– Pressure sores: Prolonged pressure on the skin can cause pressure sores, which can be painful and difficult to heal.
– Urinary and bowel problems: Bladder and bowel control can be affected, leading to incontinence or difficulty urinating.
Treatment and Management
There is no cure for a spinal cord injury; however, treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment may include:
– Surgery: Surgery can be used to stabilize the spine, relieve pressure on the spinal cord, and repair damaged tissue.
– Rehabilitation: Physical and occupational therapy can help individuals regain lost skills and learn new ways to perform tasks.
– Medications: Medications can be used to manage pain, control autonomic dysreflexia, and prevent complications.
T6 Spinal Cord Injury: Navigating Bladder and Bowel Challenges
Individuals living with a T6 spinal cord injury often face challenges in controlling bladder and bowel function. This can significantly impact their quality of life and require specialized interventions.
The T6 segment of the spinal cord is located in the upper chest region. Damage to this area can disrupt the nerve signals responsible for controlling the muscles involved in urination and defecation. As a result, individuals may experience difficulty holding or emptying their bladders and bowels.
Managing bladder and bowel function after a T6 injury typically involves a combination of medical devices, therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Some common devices include indwelling catheters to drain the bladder and suppositories or enemas to promote bowel movements.
Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction
Difficulty controlling bladder and bowel function is one of the most common challenges faced by individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries. Damage to the spinal cord at the T6 level can disrupt the nerves that control the muscles involved in urination and defecation, leading to a range of problems, including:
- Urinary incontinence: Difficulty holding or controlling the flow of urine, leading to involuntary leakage.
- Bowel incontinence: Difficulty controlling the release of stool, resulting in accidental bowel movements.
- Urinary retention: Inability to empty the bladder completely, which can lead to infection and other complications.
- Bowel constipation: Difficulty passing stool, which can cause pain, discomfort, and other health issues.
Managing bladder and bowel dysfunction after a T6 injury requires a tailored approach that may involve a combination of medical devices, therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Some common strategies include:
- Indwelling catheters: Thin tubes inserted into the bladder through the urethra to drain urine.
- Suppositories or enemas: Medications inserted into the rectum to stimulate bowel movements.
- Pelvic floor exercises: Exercises designed to strengthen the muscles that control urination and defecation.
- Dietary modifications: Adjusting diet to manage bowel function, such as increasing fiber intake for constipation or limiting fluids before bedtime to reduce nighttime urination.
- Electrical stimulation: Using electrical impulses to stimulate the nerves responsible for bladder and bowel function.
Proper management of bladder and bowel dysfunction is crucial for maintaining health, preventing complications, and improving quality of life for individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries.
T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
A T6 spinal cord injury occurs when the spinal cord is damaged at the level of the sixth thoracic vertebra. This type of injury can result in a loss of sensation and movement in the lower body, including the legs, feet, and trunk. It can also affect bowel and bladder function.
Understanding Autonomic Dysreflexia
Autonomic dysreflexia is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur in individuals with spinal cord injuries at or above the T6 level. It is characterized by an exaggerated reflex response to certain stimuli, such as bladder or bowel distension, which can lead to dangerously high blood pressure and severe headaches. If left untreated, autonomic dysreflexia can result in stroke, seizures, and even death.
Symptoms of Autonomic Dysreflexia
Recognizing the symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia is crucial for prompt intervention. These symptoms may include:
- Sudden onset of severe headache
- Profuse sweating above the level of injury
- Goosebumps or flushing of the skin
- Increased blood pressure
- Slowed or irregular heart rate
- Nasal congestion
- Blurred vision
- Nausea and vomiting
Triggering Factors of Autonomic Dysreflexia
Understanding the potential triggers of autonomic dysreflexia can help in preventing and managing this condition. Common triggers include:
- Bladder or bowel distension
- Skin irritation or injury
- Tight clothing or restrictive devices
- Pain
- Constipation
- Catheterization
- Menstruation
Managing Autonomic Dysreflexia
Immediate treatment is essential to control the symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia and prevent serious complications. The first step involves identifying and eliminating the underlying trigger. This may include emptying the bladder or bowel, removing tight clothing, or treating pain.
Medications such as calcium channel blockers or nitroprusside may be administered to lower blood pressure. In severe cases, hospitalization and intensive care may be necessary to monitor and stabilize vital signs.
Prevention and Prognosis
Preventing autonomic dysreflexia is crucial for the long-term health and well-being of individuals with spinal cord injuries. Regular bowel and bladder management programs, proper skin care, and avoiding potential triggers are essential.
The prognosis for autonomic dysreflexia depends on the severity of the spinal cord injury and the individual’s overall health. With proper management, most individuals can live full and active lives.
T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
A T6 spinal cord injury severs or damages the spinal cord at the sixth thoracic vertebra. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including paralysis, loss of sensation, and impaired breathing. While there is no cure for a T6 spinal cord injury, treatment can help to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
Treatment for a T6 spinal cord injury focuses on managing symptoms, promoting mobility, and improving quality of life. Rehabilitation is a key part of treatment and can help people with T6 spinal cord injuries to regain function and independence.
Managing Symptoms
There are a variety of medications that can be used to manage the symptoms of a T6 spinal cord injury. These medications can help to relieve pain, reduce muscle spasms, and improve bladder and bowel function. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct spinal cord damage or to relieve pressure on the spinal cord.
Promoting Mobility
Physical therapy and occupational therapy can help people with T6 spinal cord injuries to regain mobility. Physical therapy can help to strengthen muscles and improve range of motion. Occupational therapy can help people to learn how to perform everyday tasks, such as dressing, eating, and bathing.
Improving Quality of Life
There are a number of things that people with T6 spinal cord injuries can do to improve their quality of life. These include:
1. Getting involved in social activities
2. Pursuing education or employment
3. Participating in sports or hobbies
4. Joining support groups
With the right support and resources, people with T6 spinal cord injuries can live full and active lives.
T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
A T6 spinal cord injury is a serious medical condition that can have a profound impact on an individual’s life. The injury occurs when the spinal cord is damaged at the level of the sixth thoracic vertebra. This can result in a loss of mobility, sensation, and function below the level of the injury.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a T6 spinal cord injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Loss of mobility in the legs and feet
- Numbness or tingling in the legs and feet
- Loss of bowel and bladder control
- Difficulty breathing
- Pain
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Causes
T6 spinal cord injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Car accidents
- Motorcycle accidents
- Falls
- Sports injuries
The severity of the injury will depend on the location and extent of the damage to the spinal cord.
Treatment
There is no cure for a T6 spinal cord injury, but there are treatments that can help to improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment may include:
- Surgery to stabilize the spine and prevent further damage
- Physical therapy to help the patient regain mobility and function
- Occupational therapy to help the patient learn how to perform everyday tasks
- Speech therapy to help the patient improve their speech and swallowing
The goal of treatment is to help the patient achieve the highest level of function possible.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a T6 spinal cord injury depends on the severity of the injury. With proper treatment, many patients can live full and active lives. However, some patients may experience permanent disabilities and require ongoing care.
Legal Considerations
T6 spinal cord injuries can give rise to legal claims for compensation, including medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering. If you have suffered a T6 spinal cord injury, it is important to speak with an attorney to discuss your legal options.
Preventing T6 Spinal Cord Injuries
There is no surefire way to prevent T6 spinal cord injuries, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk, such as:
- Wearing a seatbelt when driving
- Wearing a helmet when riding a motorcycle
- Avoiding falls
- Playing sports safely
By taking these precautions, you can help to reduce your risk of suffering a T6 spinal cord injury.
T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
A T6 spinal cord injury, a severe trauma that can result in lifelong physical and cognitive challenges, alters a person’s life irrevocably. This complex condition affects mobility, sensation, and bodily functions, requiring extensive medical care and rehabilitation. Understanding the legal rights and available support systems is crucial for individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries and their families.
Legal Protections
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) prohibits discrimination based on disability, ensuring equal opportunities for individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries. The ADA covers employment, public accommodations, transportation, and access to government programs and services. Other laws, such as the Fair Housing Act and the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, provide additional protections in housing and education.
Medical Treatment
The severity of a T6 spinal cord injury dictates the treatment plan. Surgery may be necessary to stabilize the spine or relieve pressure on the spinal cord. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy help individuals regain function and independence. Medications manage pain, muscle spasms, and other symptoms.
Adaptive Equipment
Adaptive equipment empowers individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries to live more fulfilling lives. Wheelchairs increase mobility, while canes and walkers provide stability. Specialized beds, wheelchairs, and bathroom equipment enhance comfort and independence.
Support Groups
Connecting with others who have experienced similar challenges provides invaluable support. Spinal cord injury support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, learn from others, and access resources.
Financial Assistance
Individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries may qualify for various financial assistance programs. Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) provides monthly benefits to those who cannot work due to their disability. Medicaid and Medicare cover medical expenses, while vocational rehabilitation services help individuals return to work.
Long-Term Care Planning
Planning for long-term care is essential for individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries. This includes creating a financial plan, exploring housing options, and making legal arrangements. Caregivers play a vital role in providing assistance with daily activities and medical care.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Coping with the challenges of a T6 spinal cord injury can be emotionally and psychologically demanding. Therapy, support groups, and peer mentoring provide a safe outlet for expressing emotions and developing coping mechanisms.
Reablement
Reablement, a holistic approach to rehabilitation, empowers individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries to maximize their independence. It focuses on teaching new skills, increasing self-confidence, and promoting community integration.
Conclusion
Living with a T6 spinal cord injury is a complex and challenging journey. However, with the right medical care, support systems, and legal protections, individuals can live full and meaningful lives. By advocating for their rights and accessing available resources, they can overcome adversity and achieve their full potential.
T6 Spinal Cord Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
A T6 spinal cord injury refers to damage to the spinal cord at the level of the sixth thoracic vertebra. This type of injury can cause significant impairments, including loss of sensation and motor function in the lower body and bowel and bladder dysfunction. Living with a T6 spinal cord injury can be challenging, but there are resources and strategies available to help you regain your independence and live a fulfilling life. This article will provide you with comprehensive information on T6 spinal cord injuries, including symptoms, treatment options, and legal considerations.
Symptoms of a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
The symptoms of a T6 spinal cord injury can vary depending on the severity of the damage. Common symptoms include:
- Loss of sensation in the lower body, including the legs, feet, and groin.
- Loss of motor function in the lower body, resulting in difficulty walking, standing, or sitting.
- Bowel and bladder dysfunction, including difficulty controlling urination and defecation.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Chronic pain.
- Skin problems, such as pressure sores.
- Spasticity, or involuntary muscle contractions.
Treatment Options for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
There is no cure for a spinal cord injury, but treatments are available to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Medication to manage pain, spasticity, and other symptoms.
- Physical therapy to improve range of motion and strength.
- Occupational therapy to help you learn how to perform daily activities with your injury.
- Speech therapy to help you improve your communication skills.
- Assistive devices, such as wheelchairs, braces, and canes, to help you regain mobility.
- Surgery to repair or stabilize the spinal cord.
Rehabilitation for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
Rehabilitation is an essential part of the recovery process after a spinal cord injury. Rehabilitation can help you regain as much function as possible and learn how to live independently with your injury. Rehabilitation typically involves a team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists. Rehabilitation may take place in a hospital, rehabilitation center, or outpatient clinic.
Finding Legal Help
If you have suffered a spinal cord injury, it is important to consult with an attorney experienced in spinal cord injury law. An attorney can help you obtain appropriate compensation for your injuries and ensure that you have access to the resources and support you need. When choosing an attorney, look for someone who has a strong track record of success in spinal cord injury cases and who is committed to fighting for your rights.
Emotional Support for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
Living with a spinal cord injury can be emotionally challenging. It is important to seek emotional support from family, friends, therapists, or support groups. Talking about your feelings and experiences can help you cope with the challenges of living with a spinal cord injury. There are also many online resources and communities available to provide support and information to people with spinal cord injuries. Don’t be afraid to reach out for help when you need it.
Financial Assistance for a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
There are a number of financial assistance programs available to people with spinal cord injuries. These programs can help you pay for medical expenses, assistive devices, and other costs associated with your injury. To learn more about these programs, contact your state vocational rehabilitation agency or the Social Security Administration.
Living a Fulfilling Life with a T6 Spinal Cord Injury
Living with a spinal cord injury can be challenging, but it is possible to live a fulfilling life. With the right support and resources, you can regain your independence, pursue your goals, and enjoy life to the fullest. Don’t give up on yourself. There are many resources available to help you live a full and happy life.