Burn injuries are a common but serious type of injury that can happen to anyone at any age. They range from minor skin damage to severe, life-threatening conditions requiring specialized medical care. Understanding burns — what causes them, how they are classified, and how to treat and prevent them — is essential for safety and health.
What Are Burn Injuries?
Burn injuries occur when the skin or other body tissues are damaged by heat, chemicals, electricity, radiation, or friction. The severity depends on the cause, duration of exposure, and the part of the body affected.
Common Causes of Burn Injuries
Thermal Burns: Caused by hot objects, fire, steam, or boiling liquids. This is the most common type of burn.
Chemical Burns: Result from contact with strong acids, alkalis, or other corrosive substances.
Electrical Burns: Caused by contact with electrical current or lightning strikes. These burns often affect tissues beneath the skin.
Radiation Burns: Caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light (sunburn) or other sources of radiation like X-rays.
Friction Burns: Caused by skin rubbing against rough surfaces at high speed, such as road rash.
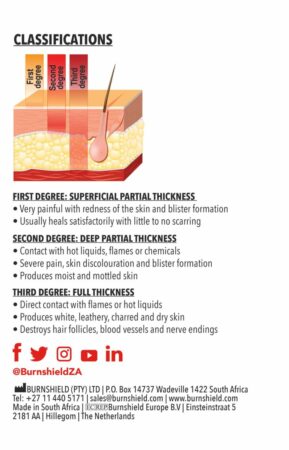
Types and Degrees of Burns
Burn injuries are classified by their depth and severity:
1. First-Degree Burns (Superficial Burns)
Affect only the outer layer of skin (epidermis).
Symptoms: Redness, mild swelling, pain, dry skin without blisters.
Examples: Mild sunburn, brief contact with hot object.
Usually heal within a week without scarring.
2. Second-Degree Burns (Partial Thickness Burns)
Affect both the outer layer and underlying layer of skin (dermis).
Symptoms: Redness, blistering, swelling, severe pain, moist appearance.
Healing time varies and may result in scarring.
3. Third-Degree Burns (Full Thickness Burns)
Destroy both the epidermis and dermis, affecting deeper tissues.
Symptoms: White, charred, or leathery skin, numbness due to nerve damage.
Require immediate medical attention and often skin grafting.
4. Fourth-Degree Burns
Extend beyond skin into muscles, bones, or tendons.
Extremely serious, life-threatening, require specialized treatment.
Symptoms and Signs of Burn Injuries
Pain or numbness
Red, white, or charred skin
Blisters
Swelling
Shock symptoms (in severe burns) such as pale, clammy skin, weakness, confusion
Immediate First Aid for Burn Injuries
Remove the person from the source of burn.
Cool the burn: Use cool (not cold) water for at least 10 minutes to reduce pain and swelling. Avoid ice or very cold water as it may worsen damage.
Protect the burn: Cover loosely with a sterile, non-stick bandage or clean cloth.
Avoid breaking blisters.
Do not apply ointments, creams, or home remedies immediately.
Seek medical help immediately for:
Large or deep burns
Burns on face, hands, feet, genitals, or major joints
Chemical or electrical burns
Signs of infection (increased redness, pus, fever)
Medical Treatment for Burn Injuries
Treatment depends on severity:
Minor burns: May only require cleaning, dressings, pain relief, and monitoring.
Severe burns: May require intravenous fluids, antibiotics, surgery (skin grafts), pain management, and rehabilitation.
Burn centers: Specialized hospitals with advanced care for extensive or complicated burns.
Long-Term Effects of Burn Injuries
Scarring and contractures (tightened skin affecting movement)
Psychological trauma, including PTSD or anxiety
Possible disability or disfigurement requiring physical therapy and counseling
Prevention Tips to Avoid Burn Injuries
Keep hot liquids and foods out of children’s reach.
Use caution around fire, stoves, heaters, and electrical appliances.
Store chemicals safely and wear protective gear when handling them.
Install smoke detectors and practice fire drills at home and work.
Avoid prolonged sun exposure and use sunscreen.
Use proper electrical safety and avoid overloaded outlets.
Conclusion
Burn injuries can range from minor annoyances to severe medical emergencies. Prompt first aid, proper medical care, and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk and impact of burns. Understanding the types, causes, and treatment of burn injuries helps you protect yourself and others.
If you or someone you know has suffered a serious burn injury, seek professional medical and legal assistance to ensure the best care and protect your rights.